What Is Reverse Logistics? Understanding the Basics
Reverse logistics is often overlooked by organisations, this 3 part series looks at what Reverse logistics is and why it is important to deal with other organisations within your supply chain who implement reverse logistics.
This is Part 1 of this series on Reverse Logistics. Here we will take a look at what Reverse Logistics is and how it works.
What is reverse logistics?
Reverse logistics refers to all procedures associated to product returns, repairs, maintenance, recycling and dismantling for products and materials. Overall it incorporates running products in reverse through the supply chain to gain maximum value.
Why is it important to deal with organisations who implement reverse logistics?
Organisations that implement reverse logistics are able to improve customer service and response times; reduce environmental impact by reducing waste and improve overall corporate citizenship.
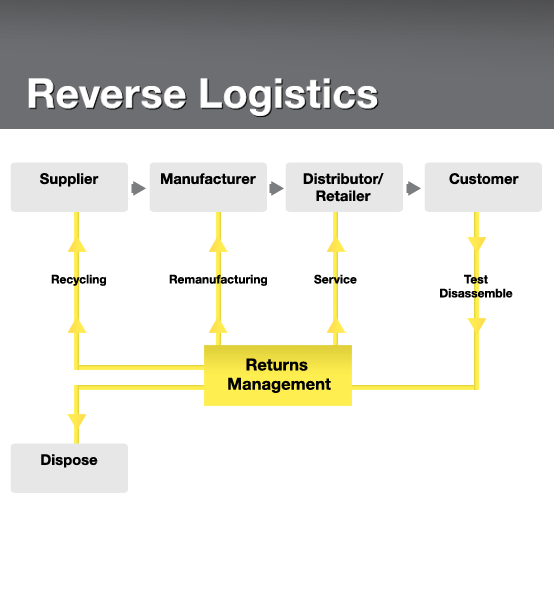
Let’s look at an example; a manufacturer produces product A which moves through the supply chain network reaching the distributor or customer. Any process or management after the sale of product A involves Reverse Logistics.
If product A happened to be defective the customer would return the product. The manufacturing firm would then have to organise shipping of the defective product, testing the product, dismantling, repairing, recycling or disposing the product.
Product A will travel in reverse through the supply chain network in order to retain any use from the defective product. This is what reverse logistics is about.